If your basement enables moisture into the area, it will probably ruin any floor your choose. What'll you would like to utilize that space of the home of yours for. Leaks that come about after a heavy rain, for example, indicate that there's something wrong with the waterproofing. Several basement flooring suggestions take into consideration the different varieties of materials to be put into use for installation.
Images about Basement Floor Slab Thickness

Water problems in the home of yours can be extremely nerve-racking since they can harm the development of the structure and they can easily in addition impact the overall health of yours. But, if the dampness is a frequent problem, it is simply a question of time before it begins to bloom underneath the carpet.
Fixing a Concrete Basement Floor American Dry

The end result will be a constant smell which will remind everybody associated with a wet dog in the house. In control climates where dampness is relatively simple carpet usually works exceptionally well. Water leaks in the basement can occur in the walls as well as on or even below the floor panels. Should you decide to acquire a drain, the area will not be functional as a living space.
Installing a Concrete Slab the Right Way – GreenBuildingAdvisor

Moisture Content Of Concrete – When Is Concrete Dry Enough?

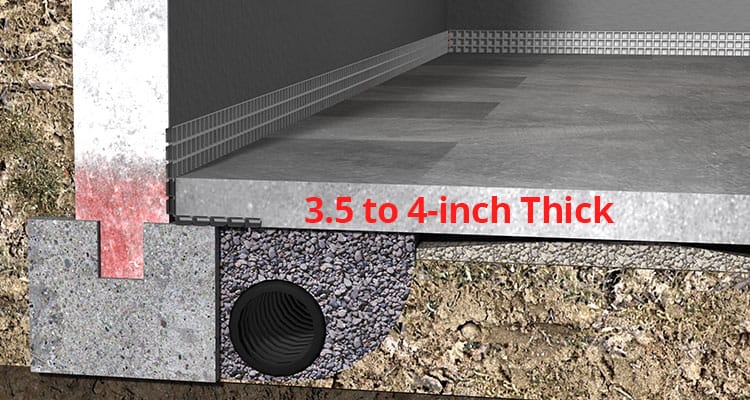
Minimum Thickness of Concrete Slab, Beam, Column, Foundation – The

Basement Floor Slab Repair Service Contractor in Hamilton, Ontario
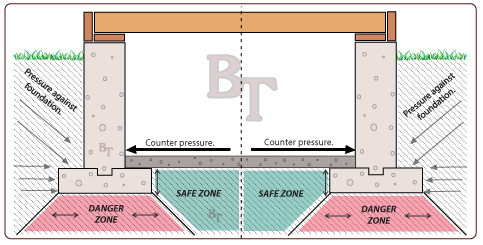
Concrete Calculator How To Calculate Concrete

Concrete slab floor construction BRANZ Renovate

Minimum Thickness of Concrete Elements Heaton Manufacturing

Concrete slab thickness commercial buildings – Cadbull
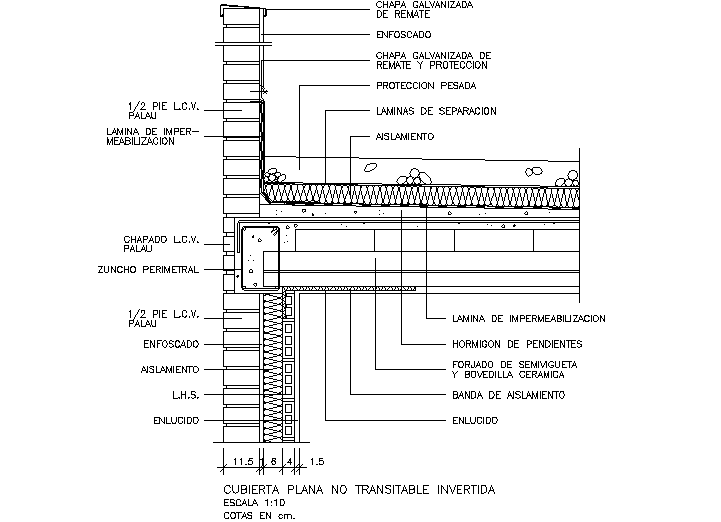
Floor Slabs WBDG – Whole Building Design Guide
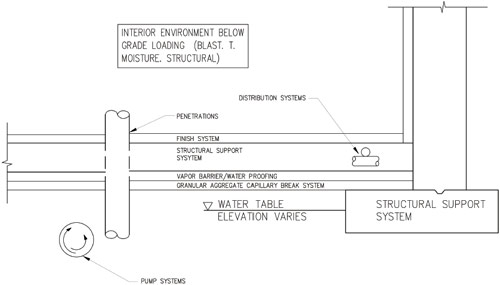
Minimum Thickness of Concrete Slab, Beam, Column, Foundation – The

BA-0309: Renovating Your Basement Building Science Corporation

3 Types of Concrete Foundations – Slab on Grade, T-Shaped, Frost
Related Posts:
- Can You Tile Over Concrete Basement Floor
- Ranch Floor Plans With Finished Basement
- Best Flooring For Basement Cement Floor
- Ceramic Tile Vs Laminate Flooring In Basement
- Walkout Basement Floor Plans Ideas
- Pouring Concrete Basement Floor
- Basement Floor Cracks Leaking
- Laminate Wood Flooring For Basement
- Waterproofing Concrete Floor Basement
- Painting A Basement Floor With Epoxy Paint
Basement Floor Slab Thickness: A Comprehensive Guide
When building or remodeling a basement, one of the most important elements to consider is the thickness of the floor slab. The thickness of the slab will affect its strength and durability, as well as its ability to withstand moisture, extreme temperatures, and other environmental factors. In this guide, we’ll explore all you need to know about basement floor slab thickness so you can make an informed decision when planning your project.
What Is a Basement Floor Slab?
A basement floor slab is a concrete structure that serves as the foundation for your basement walls and floors. It is usually poured in large sections and reinforced with metal rods or steel mesh to provide additional strength and stability. The thickness of the slab will determine its structural integrity and performance over time.
Factors That Affect Basement Floor Slab Thickness
When considering what thickness of slab to use for your basement, there are several factors that should be taken into account. These include:
• The type of soil beneath your home – Some soils are more prone to settling than others, so if you have soil that is likely to settle over time, you may need a thicker slab to ensure the structural integrity of your basement.
• The weight of any furniture or appliances that will be placed on the surface – The heavier the load, the thicker the slab needs to be in order to support it.
• The climate where you live – Different climates can cause different types of wear and tear on your slab, so you may need a thicker slab if you live in an area with extreme temperatures or high levels of precipitation.
• The intended use of your basement – If you plan to use your basement for storage or other activities that don’t require much movement or stress on the surface, then a thinner slab may suffice. But if you plan on using it for something like a gym or workshop, then a thicker slab will be necessary to handle the additional weight and stress.
Typical Dimensions for Basement Floor Slabs
The typical dimensions for a basement floor slab vary depending on several factors such as soil type, climate, and intended use. Generally speaking, slabs for residential basements typically range from 4-8 inches thick while slabs for commercial basements are usually 8-12 inches thick. However, it is always best to consult with an experienced contractor or engineer before making any final decisions about what thickness is best for your project.
Benefits of Thicker Basement Floor Slabs
Thicker slabs provide several benefits compared to thinner slabs:
• Increased durability – Thicker slabs are more resistant to cracking or settling due to their greater mass and higher density. This makes them ideal for areas where there is frequent freezing and thawing cycles or areas with heavy foot traffic.
• Improved insulation – Because they have a higher thermal mass than thinner slabs, thicker slabs are better able to maintain consistent temperatures in both hot and cold climates. This makes them ideal for areas where energy efficiency is a priority.
• Reduced noise transmission – Thicker sl Abs are better able to absorb and dampen sound waves, making them ideal for areas with high levels of ambient noise.
Overall, thicker slabs offer a number of advantages compared to thinner slabs, but it is important to consider all factors when deciding on the best thickness for your project. By consulting with an experienced contractor or engineer, you can ensure that you get the right slab thickness for your basement.
