The ideas of painting both polished concrete as well as terrazzo floors include the most important job of all, finding the best sort of paint for the job. They're the best applications for polished concrete floor surfaces as public authorities calculate the long term cost benefits of other floorings. Apart from that, the concrete floors improving supplies a sensation of security to home owners.
Images about Concrete Floor Building Regs
Polished concrete floors don't just look really good, in addition, they boast a wide range of benefits that mark them as being past some other options of flooring. The covering put on to polished flooring is glossy though it is thoroughly tested for slip resistance at all traffic levels. Earlier concrete floors which were generally known as cement floors had simply a gray and a dull appearance, but today that isn't the case.
Building Guidelines Concrete Floors, Slabs
The benefits that an individual may buy from the polished concrete floors are extremely numerous and several of them include the basic fact that the polished concrete floors supply a genuine very low cost solution to the notion of flooring as a well as providing a great alternative in conditions of environmentally friendly options.
How To Insulate An Existing Concrete Slab? BagOfConcrete
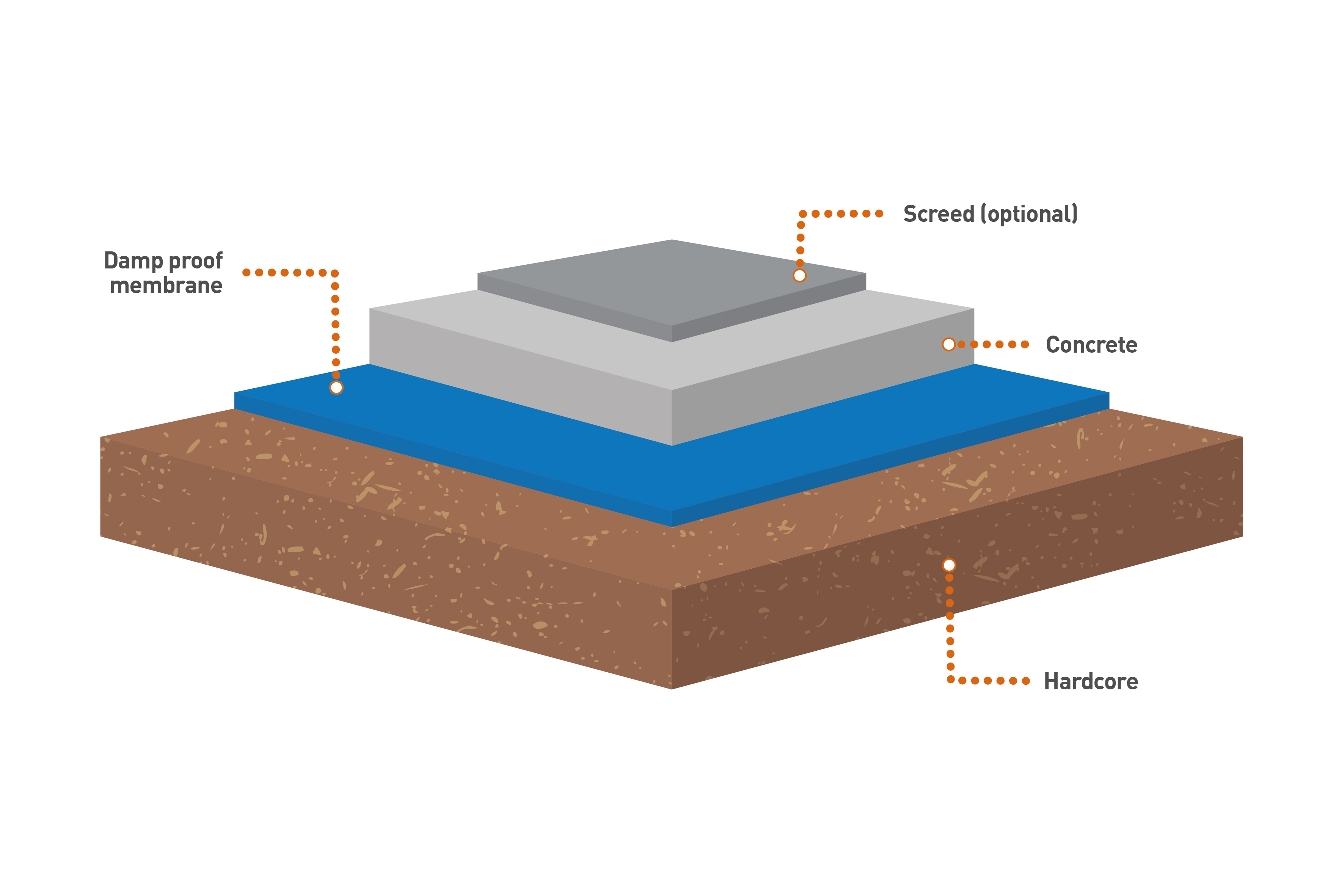
Cross section floor insulation building regulations Floor

GreenSpec: Housing Retrofit: Ground Floor Insulation
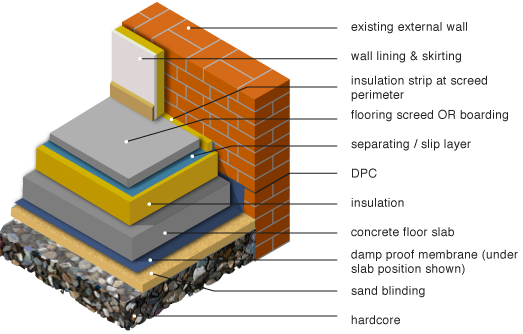
Limecrete Floor Breathable Solid Floor LABC Certified

E5MCPF23 Concrete Ground Bearing Floor, Insulation Below Slab LABC

Evolution of Building Elements
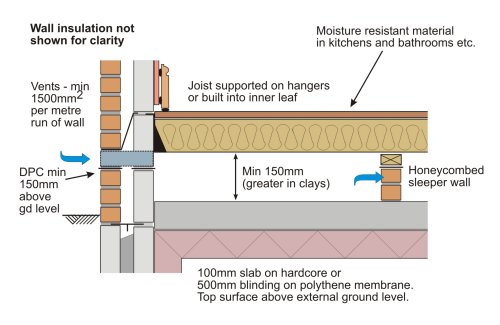
E5SMEW25 Concrete Ground Bearing Floor, Insulation below Slab LABC

Building Guidelines Suspended Timber Floors
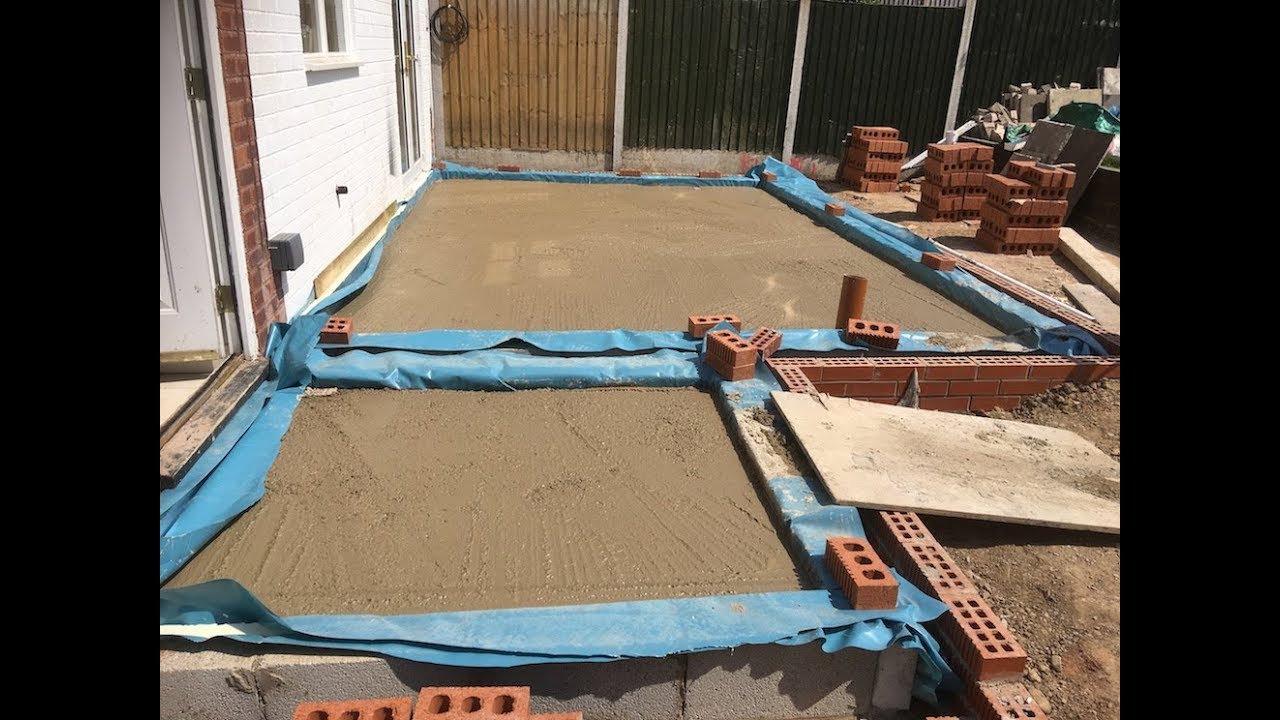
How to build an extension: part 3 concrete floor slab

Floor constructions The Irish Building Regulations Technical

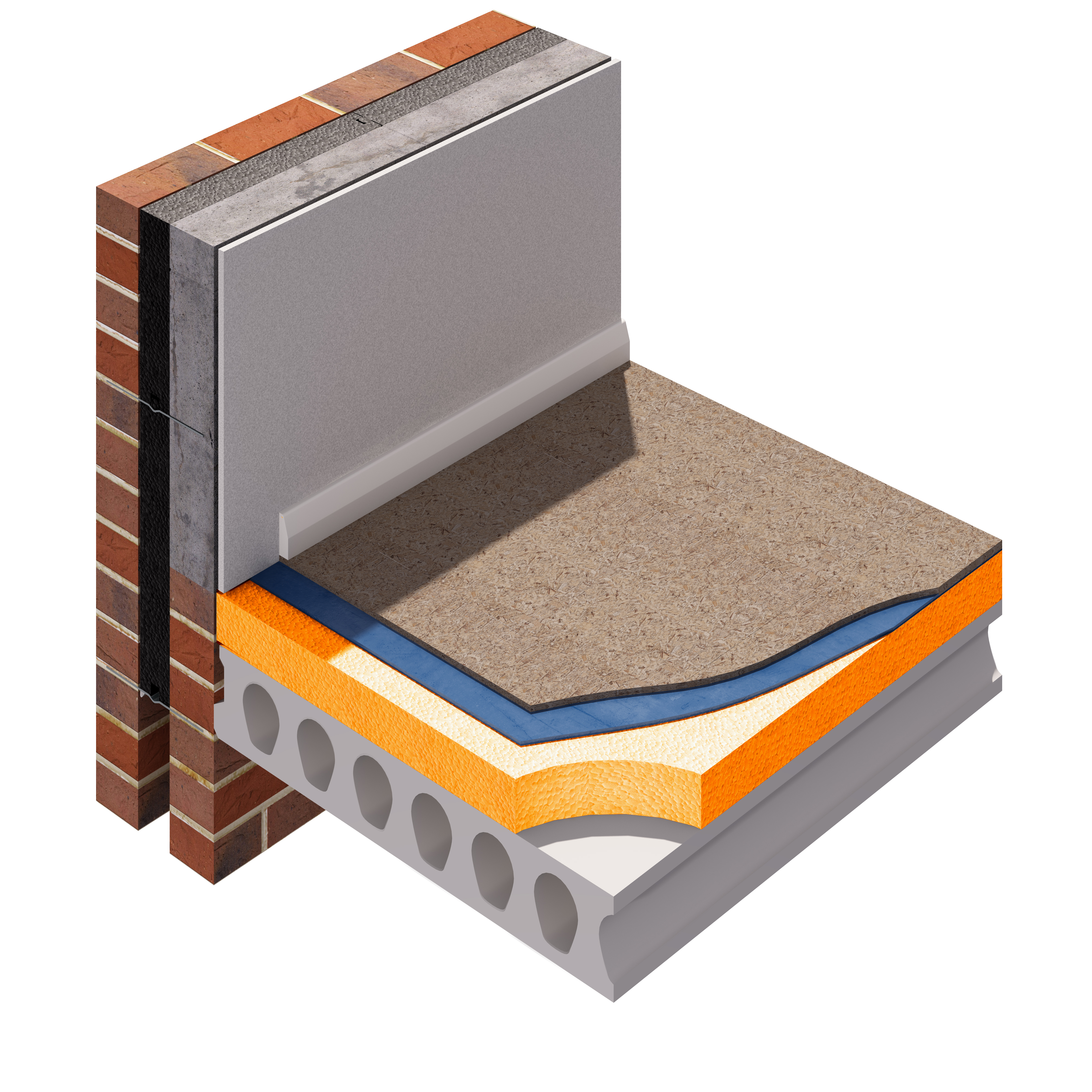
Acoustic floor insulation and Liquid Floor Screed typical construction

Insulation for ground floors – Designing Buildings
Related Posts:
- Lightweight Concrete Flooring Systems
- Pretty Concrete Floors
- Flooring Options For Concrete Floors
- Polished Concrete Floor Ideas
- Concrete Floor Washer
- Non Skid Concrete Floor Paint
- Removing Tile Glue From Concrete Floor
- How To Lay Porcelain Tiles On A Concrete Floor
- Easy Concrete Floor Ideas
- Acid Stain Concrete Floor Prep
Introduction to Concrete Floor Building Regs
Concrete floors are often required for a variety of commercial and residential projects. As such, there are certain regulations that must be followed when building a concrete floor in order to ensure the safety and longevity of the structure. In this article, we will cover the various regulations and requirements that must be met when constructing a concrete floor, as well as answer some of the most frequently asked questions about concrete floor building regulations.
Building Codes for Concrete Floors
When it comes to building a concrete floor, there are several codes that must be taken into consideration in order to ensure the safety and integrity of the structure. These codes include:
-The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) Standard 7-10: This is a set of design standards used for buildings and other structures. It outlines important design criteria such as wind loads, snow loads, seismic loads, and other environmental considerations.
-International Building Code (IBC): This code provides guidelines for the design, construction, alteration, repair and maintenance of buildings and structures. It includes requirements for materials, components, systems, and performance criteria for both new construction and existing buildings.
-International Residential Code (IRC): This code is specifically designed for residential applications. It covers topics such as foundation design, framing systems, fire safety measures, plumbing systems, electrical systems, heating systems, ventilation systems, roofing systems, insulation requirements and more.
-American Concrete Institute (ACI): ACI provides guidelines for the design of concrete floors. These guidelines include information on testing procedures, mix design specifications, curing methods and more.
-Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA): OSHA sets regulations that protect workers from dangerous working conditions in all industries including construction. This includes regulations related to fall protection when working at heights such as ladders or scaffolding.
FAQs About Concrete Floor Building Regs
Q: What is the minimum thickness that a concrete floor must be?
A: The minimum thickness required for a concrete floor depends on several factors such as the type of use it will get (i.e., light or heavy duty), the size of the room or area in which it will be installed (i.e., small or large), and any additional loadings or stresses on the floor (e.g., from equipment). Generally speaking however, a minimum thickness of 4 inches is recommended for most residential applications while 6 inches may be necessary for commercial applications or areas with heavier loadings/stresses placed upon them. Additionally, if local building codes require thicker slabs then they should always be followed.
Q: What type of reinforcement should be used in a concrete floor?
A: Reinforcement is typically used in concrete floors to increase strength and reduce cracking due to shrinkage or movement over time due to temperature changes or loading conditions. Types of reinforcement commonly used include steel bars (rebar) or wire mesh which can be embedded into the concrete during pouring or added after it has set but before it has been cured fully. The size and spacing requirements between reinforcing materials depend on local building codes as well as application specific needs such as span length or load bearing requirements.
Q: What Type of curing is recommended for concrete floor construction?
A: Curing of concrete should always be done properly to ensure the long-term strength and durability of the floor. Generally, curing should begin immediately after the concrete has been poured and should continue until the slab has reached its full strength (typically 28 days). During this time, proper moisture levels must be maintained to allow for proper hydration of the cement. This can be done by using a curing compound or covering the slab with plastic sheeting or wet burlap.