The problem is most people do not take the time frame to read through the extended warranty and are shocked whenever they find out the issue they are having with the flooring is one of the "exclusions". Installation of nearly all engineered hardwood floors are actually done by the glue down or floating floor method. You can also check the internet for some helpful information such as the hardness scale for certain wood flooring species.
Images about Engineered Hardwood Flooring Comparison

The majority of men and women selling hardwood flooring know little or no concerning wood and moisture, in case they do not even have a moisture meter, that's a sign that they're not professional and know nothing or very small about hardwood flooring and should not be selling it. Installation time can be reduced with pre finished hardwood flooring which eliminates the application and drying period of the finish and sealer.
Which Is Better? Engineered vs. Solid Hardwood Flooring
Employ a door mat so people can clean the bottoms of their shoes just before they walk on the hardwoods. The primary use to remember is the fact that a glued down floor is rigid; as soon as a floor panel is actually dried in place, it's there for good whether it is snug to the subsequent panel with or not. Cinnamon-stained, actually called cherry-stained, Asian walnut hardwood boards work with a vibrant, red hue.
Hardwood Vs. Engineered Wood Flooring u2013 Which Is Best For You

Solid Hardwood vs Engineered: How Are They Different

Solid Wood vs. Engineered Wood Flooring Comparison Guide
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/engineered-hardwood-vs-solid-flooring-1821677_0203_hardwood_engineered_0595-52ce668b14ae44e3a85ba20faa26f648.jpg)
Whatu0027s the Difference Between Solid Hardwood and Engineered

Types of Hardwood Flooring: Solid Hardwood vs. Engineered Hardwood

Flooring Faceoff: Engineered vs. Solid Hardwood Floors u2014 Scout

Engineered Wood Flooring vs Solid Hardwood Flooring ⋆ Gemini

Laminate Flooring vs. Engineered Wood Flooring: Which Is Better?
/laminate-vs-engineered-wood-flooring-comparison-1822247_hero_0269-8ef2d32f69f243e3970bbc6823bce163.jpg)
Hardwood floors Blog – KT Hardwoods, Inc.

Best Engineered Wood Flooring for Your Home

3/4″ Inch Thick Engineered. Baltic Birch Ply – 5.8 mm Wear Layer

Engineered Hardwood vs Solid Hardwood Flooring – Difference and

Related Posts:
- What Is Best To Clean Engineered Hardwood Floors
- Hardwood Flooring For Dollhouses
- Hardwood Floor Vs Engineered Wood Cost
- Engineered Hardwood Flooring Hardness Scale
- Shark Hardwood Floor Cleaning Machines
- Hickory Fireside Hardwood Flooring
- 5 Inch Walnut Hardwood Flooring
- Direct Hardwood Flooring Reviews
- Hardwood Floor Laying
- Hand Scraped Teak Hardwood Flooring
Engineered Hardwood Flooring Comparison: All You Need to Know
Engineered hardwood flooring is a popular choice for many homeowners. It’s durable, looks beautiful, and provides a timeless look to any room in the home. But when it comes time to choose the right engineered hardwood flooring, there are several factors to consider. This article will provide an in-depth comparison of the different types of engineered hardwood flooring available on the market today.
Types of Engineered Hardwood Flooring
When looking at engineered hardwood flooring, there are three main types to consider: solid-core, multi-layer, and vinyl-clad. Each type offers its own benefits and drawbacks and is best suited for certain situations or areas of the home.
Solid-Core: Solid-core engineered wood flooring is made from one layer of wood veneer that is bonded to a core material such as plywood or medium density fiberboard (MDF). This type of flooring is the most stable and durable type of engineered hardwood since it has no joints or seams that can be affected by moisture or temperature changes. It also requires less maintenance than other types of engineered hardwood since it is already sealed with a protective coating.
Multi-Layer: Multi-layer engineered wood flooring is made from multiple layers of wood veneer bonded together with adhesive. This type of flooring has more stability than solid-core engineered wood but may not be as durable as solid-core since there are more joints and seams present. However, multi-layer engineered wood can also be sanded and refinished multiple times over its lifetime so it may be a better option for those looking for a longer lasting solution.
Vinyl-Clad: Vinyl-clad engineered wood flooring is made from thin layers of vinyl laminated onto a core material such as plywood or MDF. This type of flooring offers better protection against moisture damage since it is completely sealed with a waterproof coating. However, vinyl-clad floors may not have the same durability as solid-core or multi-layer floors since they cannot be sanded and refinished multiple times over their lifetime.
Pros and Cons of Engineered Hardwood Flooring Comparison
When comparing different types of engineered hardwood flooring, it’s important to consider the pros and cons associated with each one. Below we’ve outlined some key points to keep in mind when making your decision:
Solid-Core: Pros – Stable and durable; Requires less maintenance; Can be sanded and refinished multiple times over its lifetime; Offers timeless look; Can be installed directly over concrete or other subfloors without additional preparation work. Cons – More expensive than other types of engineered hardwood; Not suitable for areas prone to moisture damage; Limited range in terms of style options available.
Multi-Layer: Pros – More stable than solid core; Can be sanded and refinished multiple times over its lifetime; Offers more style options than solid core; Generally less expensive than solid core. Cons – Not as durable as solid core; More susceptible to moisture damage due to seams and joints present; May require more maintenance over time due to additional seams and joints; More difficult to install than solid core due to additional prep Work required.
Vinyl-Clad: Pros – Completely sealed with a waterproof coating; More resistant to moisture damage; Easier to install than solid core or multi-layer floors; Generally less expensive than solid core or multi-layer floors. Cons – Cannot be sanded and refinished multiple times over its lifetime; Limited range in terms of style options available; May require more maintenance over time due to additional seams and joints.
What are the differences between engineered hardwood and solid hardwood?
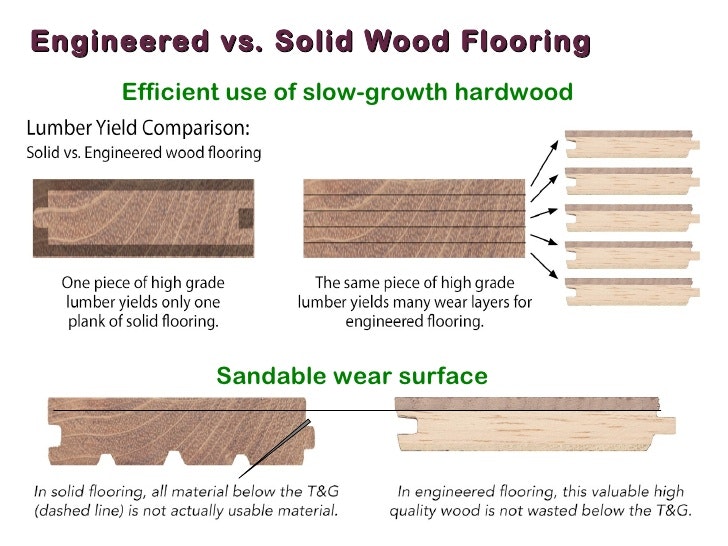
Engineered hardwood is created by layering multiple layers of wood together and bonding them with adhesives. The core layer is typically composed of softer woods like pine, while the top layer is made of a hardwood such as oak or maple. Engineered hardwood is often more stable and can be installed in areas prone to moisture or humidity.Solid hardwood is just that – a single solid piece of wood. It is usually milled from a single type of hardwood, such as oak, maple, or cherry. Solid hardwood floors are usually nailed down to a subfloor and can be sanded and refinished multiple times throughout its lifetime. Because it is a solid piece of wood, it will expand and contract with changes in humidity.